Getting started on Android
Installation
IDE integration
This new release now fully support Gradle build system and is therefore fully compatible with Android Studio. Nevertheless if you want to use the output .aar file in Eclipse ADT this link will explain you the process to follow : Consuming AARs from Eclipse.
Looking for an older version?
You can get an older version of the SDK in the Downloads section.
Project setup
Insiteo's API is provided as a single Android ARchive (.aar) file. In Android Studio you can easily import this archive by right clicking on your project -> new -> module and select 'Import JAR or AAR Package'.
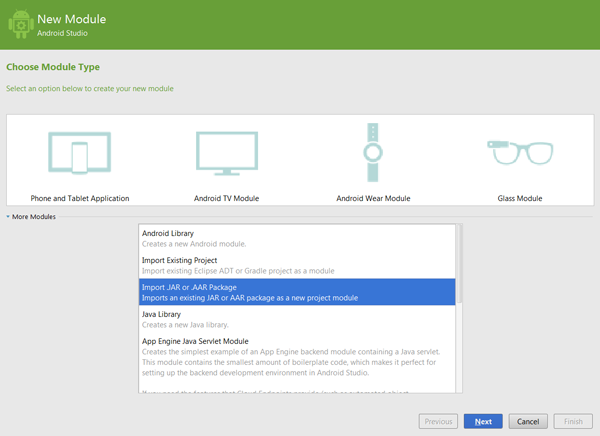
Requirements
Furthermore in order to grant all required access to our API you will need to add the following permissions to your android
AndroidManifest.xml
between the
<manifest> <manifest/>
tag :
// Required for global API use
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
// Required for Location purposes (GPS, WIFI and BLE scan)
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
In order to use our location service you also have to add its declaration to your android
AndroidManifest.xml
between the
<application> <application/>
tag :
// CAUTION: make sure to declare the location service.
<service android:name="com.insiteo.lbs.location.LocationService" />
Supported architecture and OS
Our library is compatible from
Android API 9
(ie Android 2.3) and up to recent one and supports the following
architecture:
armeabi
,
armeabi-v7a
and
x86
.
Initialization
Start the API
Don't forget your API key
Before any interaction with Insiteo's API you must set your API KEY
via
InitProvider.getInstance().setAPIKey(API_KEY);. This key can be found in your INSITEO account on the back office.
The first step to access Insiteo's services, is to initialize our API via the InitProvider singleton. This will be done with the startAPI and we will give you the data to pass (ie the EServerType, the site identifier and the language).
Use the appropriate server type
The initialization process requires a EServerType that can take the following values :
EServerType.DEV,
EServerType.TEST or
EServerType.PROD.
Depending on its values the downloaded data will be stored under the appropriate folder on the SD Card (respectively 'insiteo/sites/dev', 'insiteo/sites/test'
and 'insiteo/sites/release').
Choose your render mode
In order to get ready to use our map module, you will need to specify the render mode you plan to use. You can choose between ERenderMode2D and ERenderMode3D. Please note that the default mode is ERenderMode2D .
You can now safely start Insiteo API by calling startAPI, with an IInitListener to be notify.
private void initAPI() {
InitProvider initProvider = InitProvider.getInstance();
// Make sure to provide your API key before initializing our API
initProvider.setAPIKey(InsiteoConf.API_KEY);
// Start Insiteo API initialization (asynchronous), and get the running initialization task
initProvider.start(Activity.this, InsiteoConf.SERVER, InsiteoConf.SITE_ID, InsiteoConf.LANG, this, InsiteoConf.RENDER_MODE);
}
/**
Callback received on API server initialization.
Caution: This callback is not alway triggered on the UI thread.
*/
@Override
public Stack onInitDone(InsiteoError aError, Stack packageToUpdate) {
/* If the error is different from null then it means that the initialization has failed. Most likely this comes from a wrong API key or no network access. A failure in the API initialization does not mean that our services are unavailable. As we work with data package this only mean that you might not be using the last version of the server data. Nevertheless if you have old data you can still take advantage of our services (only some services such as Meetme won't be available as they request server interaction).
Caution: Be sure to check that you have the required package data before using our services. */
if(aError != null) {
// Handle error cases.
return null;
}
/* The error is null and the stack of packages to update is empty, this means that your application is already using the most up to date set of data. You can use all the services normally. */
else if(packageToUpdate.isEmpty()) {
// Use Location Based Services.
return null;
}
/* Initialization succeeded and new data are available. If the application is launched for the first time the data will be required for the application to work (for example to download the map tiles, the location data and so on) so the download process must be triggered. Otherwise those data are optional and can still work with old values. If you want to automatically start the download process you can return a stack of package to download (it is up to you to filter the list at your convenience), otherwise you can trigger the download later, after a specific user interaction for example. */
else {
return (AUTOMATIC_DOWNLOAD) ? packageToUpdate : null;
}
}
/**
Packages are being updated, you can, for example, use this callback to display a progress bar
*/
@Override
public void onPackageUpdateProgress(EPackageType packageType, boolean download, long progress, long total) {
if(download) {
/** For the download process the progress is given in bytes */
} else {
/** For the install process the progress is given in number of files */
}
}
/**
Callback received when the entire process of data update is done.
*/
@Override
public void onDataUpdateDone(boolean aSuccess, InsiteoError aError) {
}
Update only what you need
You can also call the update method with a list of specific package to update but they must be at least in the list of getPackagesToUpdate().
Deleting your local data
If your want to delete all the package data that were downloaded you have to remove the 'insiteo/sites/{server}/{site_id}' directories from you SD card.
Map
Map3DView now available!
In this 3.3.0_RC0 version, you can now use the Map3DView class.
Packages dependencies
Be aware that you need to have installed at least the following packages:
-
A
MAPDATApackage, which contains maps information such as zoom levels and scales. -
2D A
TILESpackage, which contains3cmfiles that will be displayed. -
3D A
MAP3DPACKAGEpackage, which contains all 3D files used for the rendering.
InitProvider.getInstance().hasPackage(EPackageType.MAP_DATA);.
Display a MapView
A MapView is provided and can be used to display a 2D/3D map component with specific interactive areas. The API also provides advanced features such as additional rendering layouts management (promotional, special areas etc …) or specific events handling. To use this component you have to make sure that you have downloaded all the required packages.
The MapView will display a 2D tiled map or 3D plane of the site (depending on your ERenderMode), and provide common map interaction (such as move, center, and pinch to zoom), animation and more. It also handle the Zone rendering and touch behavior.
The Map3DView uses the JPCT Android engine and you can refer to its documentation here.
MapAPI, you will need to instanciate a Map2DView or a Map3DView (you can not use both instance simultaneously):
//Map2DView initialization in JAVA
Map2DView mMapView = new Map2DView(getActivity());
// or in xml
<com.insiteo.map.Map2DView
android:id="@+id/insiteo_map"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
Prerequisites
-
You will need to initialize
InitProviderbefore instantiatingMapView. -
MapViewevents will be notified via theIMapListenerinterface. The singleIMapListenerassociated to the map is by default theContextthat created it (theActivityin most cases) but can be change with theMapView#setListener(IMapListener aListener)method (useful when your using theMapViewin aFragment).
Adding graphical objects on map
The MapView also allows you to display custom interactive objects. This can be done by implementing the renderer interface IRenderer and the Render Touch Object interface IRTO or by simply extending the GenericRenderer and GenericRTO that already provide common behavior (icon and label rendering, touch handling and so on, you can check their behavior in our SampleApp).
The MapView will also detect touches, and dispatch them to all IRTO. A listener can be set on the map view, to be notified of clicks on specific IRTO class (see MapView class documentation).
GenericRTO to the MapView and listening for their events:
/* This method will add the rto at the map center */
GenericRto genericRTO = new GenericRTO(mapView.getScreenCenter(), "MyRTO");
mapView.addRTO(genericRTO);
/* And to remove it */
mapView.removeRTO(genericRTO);
/* This method will add the rto to the given zone */
GenericRto genericRTO = new GenericRTO(mapView.getScreenCenter(), "MyRTO");
genericRTO.setLabel("MyRTO");
mapView.addRTOInZone(zoneId, genericRTO);
/* And to remove it */
mapView.removeRTOFromZone(zoneId, genericRTO);
/* Add a listener for this type of IRTO */
mMapView.setRTOListener(listener, GfxRto.class);
Create your own IRenderer
A renderer is a class that defines drawing and touch behavior for a certain type of IRTO. Once added to the MapView a renderer will have its render2D or render3D method call by the map rendering loop to enable to do its rendering operation and it will also be notify when to handle touch events (onTouchDown, onTouchPointerDown, onTouchMove, onTouchPointerUp, onTouchUp). If you want to use your own customized renderer, you will need to create a class that implements the IRenderer interface. Then you will be able to specify your own renderering and touch behavior.
IRenderer uses a priority value that will define it's 2D rendering and touch order. Highest priority renderered last (so on the top) and notify by touch first.
/* How to add a custom renderer */
mapView.addRenderer(myCustomRenderer);
Create your own IRTO
IRTO interface. Then you will be able to specify your object's behavior through methods like:
/* The method you will need to override in order to manually manage your object 2D rendering */
public void render2D(Canvas aCanvas, double aRatio, Point aOffset, float aAngle) {
}
/* The method you will need to override in order to manually manage your object 3D rendering */
public void render3D(ISWorld world, FrameBuffer frameBuffer, Map map, double ratio, float angle) {
}
/* Because once added to the world a 3D object will always be drawn it is up to you to remove the object from the world when required */
public void remove3DObject(ISWorld world) {
}
/* Method that gets called when the IRTO have to handle a touch down event */
public ETouchObjectResult onTouchDown(Touch aTouch) {
}
Where to find my IRTO?
All IRTO of class corresponding to the custom renderer class, when added via MapView, will be put in custom renderer. If you add an IRTO and there are no IRenderer defined for that specific class, the MapView will automatically create a GenericRenderer to handle it. So creating your own IRTO does not mean that you necessarily have to create you own IRenderer.
Zone offsets in 3D
In 3D, you can specify an offset through the z axis still by using the following method mapView.addRTOInZone(zoneId, rto, zoneOffset).
Link with external content
With the Insiteo API, you can link your content to our zone based system. To do that you will have to register this content through our back office. For example you can link a shop to one of our zone and then, get back this content in your application, simply by requesting our API.
Insiteo Interactive maps - 2 minutes tutorial
MapDBHelper class like so:
// Get all Zone/POI assocations for a given external identifier
List<ZonePoi> zonePois = MapDBHelper.getZoneAssocFromExtPoi(extPoiID);
Important
A list is returned, because you can link a POI to several zones and a zone can contains several POIs.
MapDBHelper class like so:
//Get all external Zone/POI assocations for a given zone identifier
List<ZonePoi> zonePois = MapDBHelper.getPoiAssocFromZone(zoneId, isExternal);
Each method returns an ZonePoiAssoc object which contains a position in meters and an offset (if specified) in order to place your on IRTO on our map.
Zone/Poi associations offsets
-
If you want an offset to be used when drawing an
IRTOin aZoneyou have to explicitly set it we adding theIRTOto theMapView.
Best practice
It is best practice to call the MapView onPause and onResume methods in your Activity or Fragment respective methods.
Location
Packages dependencies
If you intend to use the this service you have to make sure that the
location package have been properly downloaded.
You can easily check if the package is available on the device with the following method:
InitProvider.getInstance().hasPackage(EPackageType.LOCATION);.
Location process
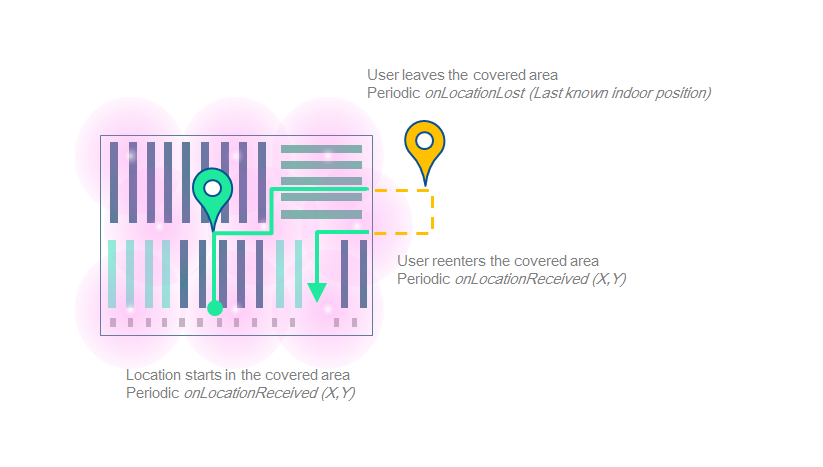
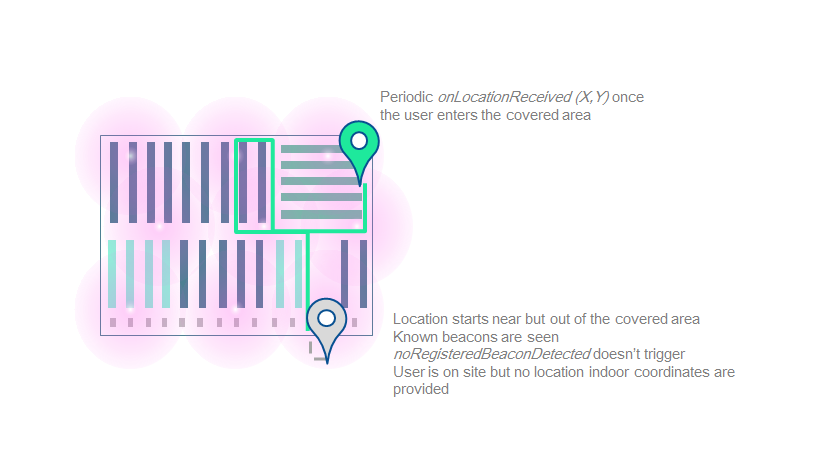
Get your first location
You can use our
LocationAPI
to obtain location information. The
LocationAPI
needs initialization information in order to communicate with our servers. You can easily link this library to the INSITEO map, so the location can be displayed on it.
LocationAPI
, you will need to create an
LocationProvider instance . To receive location, you will need to start the
LocationProvider,
with a context and an
ILocationListener. This listener will receive location events. You also have to set flags indicating location behavior, and a default map identifier:
// Retrieve the LocationProvider singleton
LocationProvider locProvider = LocationProvider.getInstance();
// And start the location process with the required flags.
locProvider.start(getActivity(), this, InsiteoConf.LOCATION_FLAGS);
// Add location renderer to the MapView so that location is automatically displayed.
mMapView.addRenderer((LocationRenderer)LocationProvider.getInstance().getRenderer(getResources()););
Which flags to use
Please contact us to get the appropriate location settings.
Prerequisites
- The API needs to be initialized.
- You can now be notified when no registered beacons were detected, which probably means that the user started the location whereas he is not on site.
Available services
Available location-based services are:
-
ELocationModule.ITINERARY: this module computes the route between an arrival point, and a departure point (could be the user current location). -
ELocationModule.GEOFENCING: this module detects when user location is in "active" areas, and notify the application that the user entered/stayed in/left these areas.
Get a specific LBS module
To use them, you have to request them from
LocationProvider with the
getModule method.
Be aware that a new module is created for each call of
getModule.
Itinerary
Packages dependencies
If you intend to use the this service you have to make sure that the
itinerary
package have been properly downloaded.
You can easily check if the package is available on the device with the following method:
InitProvider.getInstance().hasPackage(EPackageType.ITINERARY);.
Enable itinerary rendering
Itinerary
or
Geofencing
you have to get the module from the location provider. If you want it to be displayed on an INSITEO map, do as follow:
// Retrieve the itinerary module from the LocationProvider
mItineraryProvider = (ItineraryProvider) LocationProvider.getInstance().getModule(ELocationModule.ITINERARY);
// get itinerary renderer linked to provider
mItineraryRenderer = (ItineraryRenderer) mItineraryProvider.getRenderer(getResources());
mItineraryRenderer.setPriority(10);
// Add this renderer to the map renderers list
mMapView.addRenderer(mItineraryRenderer);
// Register for itinerary rendering user interaction (such as clicks).
mItineraryRenderer.setListener(this);
Request an itinerary between two points
// Request an itinerary between two points.
Position departure = new Position(startMapId, 40, 40);
Position arrival = new Position(destMapId, 168, 100);
mItineraryProvider.requestItinerary(departure, arrival, this, PMR_ENABLED);
Retrieve itinerary requests
An
ItineraryRequest is returned in order to identify sender through callbacks.
Request an itinerary from user location
// Request an itinerary from the user location to a point arrival.
// With USE_LAST_LOC, you can decide to use the last location or wait for a new one.
// With PMR_ENABLED, you can set the itinerary to use only path for disabled persons.
Position arrival = new Position(mapID, 168, 100);
mItineraryProvider.requestItineraryFromCurrentLocation(arrival, USE_LAST_LOC, this, PMR_ENABLED);
Request an optimized route
// Request an optimized route between several positions (an OptimizeRequest is returned)
mItineraryProvider.requestOptimizedItinerary(pos, EOptimizationMode.EOptimizationModeNearestNeighbourShortestPath, true, false, this, false);
Request parameters
You can specify if you want to keep the first position, last position, or both.
Otpimization modes
There are multiple optimization modes available but we highly recommend to keep
EOptimizationMode.EOptimizationModeNearestNeighbourShortestPath as the default one.
Recomputation
/**
* Callback fired when the itinerary of the last request changed (when location is updated for example).
* This method can be used to ask for a new itinerary if the user is now too far from the itinerary (we usually recompute
* the itinerary over a distance of 5 meters).
* @param aRequest the related request
* @param aDistanceToIti the distance between the user location and the itinerary (in meter)
*/
@Override
public void onItineraryChanged(BaseRequest aRequest, float aDistanceToIti) {
if (aRequest instanceof ItineraryRequest && LocationProvider.getInstance().isStarted()) {
if (aDistanceToIti > MAX_RECOMPUTATION_DISTANCE || aDistanceToIti == -1) {
aRequest.recompute();
}
}
}
Prerequisites
Make sure to have the dynamic mode to
true
to have the
onItineraryChanged
triggered (see
ItineraryProvider.setDynamicMode(boolean enabled)).
When to recompute?
We usually use
5.0
meters as
MAX_RECOMPUTATION_DISTANCE
.
Geofencing
Packages dependencies
If you intend to use this service you have to make sure that the
geofencing
package have been properly downloaded.
You can easily check if the package is available on the device with the following method:
InitProvider.getInstance().hasPackage(EPackageType.GEOFENCING);.
Start the Geofencing module
Geofencing
module, you just have to retrieve the instance from the LocationProvider and register as a IGeofenceListener.
// Retrieve the geofencing module
mGeofenceProvider = (GeofenceProvider) LocationProvider.getInstance().getModule(ELocationModule.GEOFENCING);
// Register as a IGeofenceListener
mGeofenceProvider.setListener(this);
Understand geonotifications
GeofenceArea.
- The first one contains all areas the user just entered
- The second one contains all areas where the user still is and has spent a certain time .
- The third one contains all areas the user just left.
/**
* Called when geofencing module has new data available.
* @param aEnteredAreas list of areas that location has just entered
* @param aStayedAreas list of areas where location has stayed for a certain amount of time
* @param aLeftAreas list of areas that location has just left
*/
@Override
public void onGeofenceUpdate(List aEnteredAreas, List aStayedAreas, List aLeftAreas) {
Log.d("Geofencing", " onGeofenceUpdate: " + aEnteredAreas.size() + ", "
+ aStayedAreas.size() + ", " + aLeftAreas.size());
}
Dynamic Geopush
In the last version of our API, geopush content can be added to the
GeofenceProvider directly from your application in addition to the one fetched from the server. This enables, for example, your content to be more accurate to a specific user's behaviour or using context.
-
The created
GeofenceArea's polygon will be based on the specific Zone parameters that have to be provided in the back office. -
If the
GeofenceAreaparameters (ie width, enteredTime, enteredEnabled ... ) are not set they will be fetched from the configuration file. This configuration file defines those parameters by Map and not by Zone. -
If the creation succeeded the
GeofenceAreawill be automatically added to the GeofenceProvider.
Adding content to a specific
Zone or for a specific
ZonePoi
GeofenceArea width will be created and this
GeofenceArea will be automatically added to the
GeofenceProvider
// For a Zone
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(int zoneId, String content);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(int zoneId, String content, long eventTime);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(int zoneId, String content, boolean enteredEnabled, long enteredTime, boolean stayedEnabled, long stayedTime, boolean leaveEnabled, long leaveTime, float width);
// For a ZonePoi association
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(ZonePoi zonePoi, String content);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(ZonePoi zonePoi, String content, long eventTime);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(ZonePoi zonePoi, String content, boolean enteredEnabled, long enteredTime, boolean stayedEnabled, long stayedTime, boolean leaveEnabled, long leaveTime, float width);
Adding content for at a
Position
Position, you can use the methods shown below.
A square of size the on the given in parameter (or by default 4 time the size defined in the configuration file) and center on the given position will be created.
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(String guid, Position center, String content);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(String guid, Position center, String content, long eventTime);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(String guid, Position center, String content, boolean enteredEnabled, long enteredTime, boolean stayedEnabled, long stayedTime, boolean leaveEnabled, long leaveTime);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(String guid, Position center, float size, String content);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(String guid, Position center, float size, String content, long eventTime);
public GeofenceArea addGeofenceArea(String guid, Position center, float size, String content, boolean enteredEnabled, long enteredTime, boolean stayedEnabled, long stayedTime, boolean leaveEnabled, long leaveTime);
Removing a dynamic
GeofenceArea
GeofenceArea from the
GeofenceProvider call the appropriate remove method based on how it was added.
public void removeGeofenceArea(String guid);
public void removeGeofenceArea(int zoneId);
public void removeGeofenceArea(ZonePoi zonePoi);
public void removeGeofenceArea(GeofenceArea area);
Geofencing rendering :
In this new version 3.2.2 you can now view your GeofenceArea on you MapView. Like all other LBS services, you will have to retrieve its IRenderer and pass it to the MapView. All the geofencing zone will be displayed ie the one define in the back office and the one created dynamically.
Analytics
Packages dependencies
If you intend to use this service you have to make sure that the
analytics
package have been properly downloaded.
You can easily check if the package is available on the device with the following method:
InitProvider.getInstance().hasPackage(EPackageType.ANALYTICS);.
Production vs Development
In order to be able to differentiate data from an application in a testing environment from a release one Insiteo's SDK uses the
CommonConstants.DEBUG.
You should make sure to set this tag to false for your release version.
Starting the Analytics service
In order to use the analytics service you have to make sure it gets started during the API initialization. If you did not specify the analytics behavior in the API initialization method the service will be started automatically if the packages depedencies prerequisite is met. Otherwise this will depends on the value passed as the analyticsAutoStart as true will try to start it and false will keep it turned off and no data will be stored during the session.
Location events
If you have decided to use the analytics service then the user's location will be automatically sent for datamining analysis. In order to avoid internet requests overload location will be aggregated according to a given frequency that can be set in the back office.
Generic events
For any other type of events you would like to keep track of you can use the
AnalyticsGenericEvent. This event
enables you to add up to 2 Strings, 2 Integers, 2 Doubles, 2
Positions
and a label to match most cases.
AnalyticsGenericEvent
to the
AnalyticsManager.
AnalyticsGenericEvent event = new AnalyticsGenericEvent("generic_event");
zoneEvent.setString1("product a");
zoneEvent.setPos1(aLocation.getPosition());
AnalyticsManager.getInstance().addGenericEvent(event);
Insiteo's API already trace some basic events among them:
- Location start and stop
- Geofence entered, stayed and left
-
Map changes, zone clicks and
IRTOadded withZonePoi - Itinerary requests
Tracking products displayed on map
If you want to trace when a product is added to the map you can use
addRTOInZone(IRTO, ZonePoi).
This will generate a
AnalyticsGenericEvent
with the String1 set with the external id of the Poi defined in the
ZonePoi.
Completing a generic event
In can be useful in some cases to add information to a
AnalyticsGenericEvent for that you must set a
IAnalyticsListener that will be notified everytime a new generic
event is added. Returning false in this method will dismiss the event.